| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- 그리디
- kotlin
- 스프링
- 애자일기법
- 그리디알고리즘
- 읽기쉬운코드
- API
- Spring
- Baekjoon
- database
- 애자일프로그래밍
- 백준
- 클린코드
- framework
- 개발자
- 프레임워크
- 엘라스틱서치
- 코딩
- JPA
- 코드
- ES
- spring boot
- cleancode
- 자바
- Java
- 개발
- 알고리즘
- 코딩테스트
- Elasticsearch
- 데이터베이스
- Today
- Total
튼튼발자 개발 성장기🏋️
배치 처리 테스트하기 본문
단위 테스트
JUnit과 Mockito를 사용한 단위 테스트를 알아보는 시간~😄
JUnit 테스트는 테스트 케이스라고도 하는데 클래스 레벨에서 특정 기능을 테스트하는 것으로써 클래스 당 하나 이상의 테스트 케이스를 가진다.
import org. junit. jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
public class StringTest {
@Test
public void testStringEquals() {
String michael = "Michael";
String michael2 = michael;
String michael3 = new String("Michael");
String michael4 = "Michael";
assertTrue(michael == michael2);
assertFalse(michael == michael3);
assertTrue(michael.equals(michael2));
assertTrue(michael.equals(michael3));
assertTrue(michael == michael4);
assertTrue(michael.equals(michael4));
}
}- JUnit 테스트는 자바 객체로써 특정 클래스를 상속할 필요가 없고 JUnit이 클래스에게 강제하는 유일한 요구 사항은 생성자가 argument를 갖지 않아야 한다.
- 각 테스트는 public 이고 void이며 argument를 갖지 않아야한다.
- JUnit이 실행해야하는 테스트 메서드임을 나타내는 @Test 어노테이션
- assert 메서드를 사용해 유효성 검증
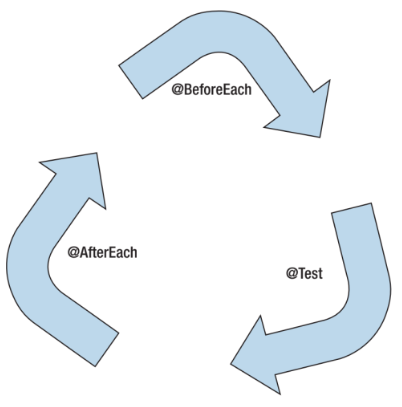
- 각각의 테스트 메서드 실행 이전에 특정 메서드를 실행하려면 메서드 레벨의 @BeforeEach
- 각각의 테스트 메서드 실행 이후에 특정 메서드를 실행하려면 메서드 레벨의 @AfterEach
- 마찬가지로 public이면서 void 이어야하고 argument를 갖지 않아야한다.
public class FooTest {
private Foo fooInstance;
@BeforeEach
public void setUp() {
fooInstance = new Foo();
}
@Test
public void testBar() {
String results = fooInstance.bar();
assertNotNull("Results were null", results);
assertEquals("The test was not a success", “success”, results);
}
@AfterEach
public void tearDown() {
fooInstance.close();
}
}그 외에도 테스트 클래스 내의 어떠한 메서드도 실행되기 전에 단 한 번만 실행되어야하는 경우에 사용하는 @BeforeAll
테스트를 하지않고 무시할 수 있는 @Ignore 테스트 케이스를 실행하는 클래스를 JUnit이 제공하는 클래스가 아닌 다른 클래스로 지정하고 싶을 때 사용하는 @RunWith
참고 :
https://junit.org/junit5/docs/current/user-guide/#writing-tests
JDBC와 DB를 이용할 때 DAO와 ItemStream 관련 테스트를 할 수 있게 해주는 것이 바로 Mock 객체다.
스텁(Stub)은 테스트에서 사용되는 하드코딩된 구현체로, 런타임 시에 필요한 동작을 정의할 수 있는 Mock 객체가 재사용 가능한 구조인 경우 사용
Mock 객체는 프록시 기반 방식과 클래스 재매핑 방식으로 동작한다.
프록시 기반 방식
- Mock 프레임워크를 사용해 프록시 객체 생성
- 프록시 객체를 필요로 하는 객체에게 setter 또는 생성자를 통해 세팅
- 외부 수단을 통해 의존성을 설정할 수 있어야 한다는 문제점이 보이죠? 스프링과 같은 의존성 주입 프레임워크를 사용해야 어떤 코드도 수정하지 않고 프록시 객체를 주입할 수 있게 해준다.
클래스 재매핑 방식
- 클래스 로더 내의 클래스 파일을 재매핑
- 프록시 기반 방식보다 강력한 기능을 제공하지만 클래스 로더에 대해 이해하는 것이 더 어려울 수 있다
Mockito: 확인이 필요한 동작을 mocking해 중요한 동작만 검증한다.
아래 코드를 보면 테스트 클래스 내부에서 생성되는 CustomerItemValidator 클래스와 의존성 주입을 받는 NamedParameterJdbcTemplate 클래스, 두 개의 애트리뷰트가 존재한다.
// JOB CODE
@Component
public class CustomerItemValidator implements Validator<CustomerUpdate> {
private final NamedParameterJdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
private static final String FIND_CUSTOMER = "SELECT COUNT(*) FROM CUSTOMER WHERE customer_id = :id";
public CustomerItemValidator(NamedParameterJdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this. jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
@0Override
public void validate(CustomerUpdate customer) throws ValidationException {
Map<String, Long> parameterMap = Collections.singletonMap("id", customer.getCustomerId());
Long count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(FIND_CUSTOMER, parameterMap, Long.class);
if(count == 0) {
throw new ValidationException(String.format("Customer id %s was not able to be found", customer.getCustomerId()));
}
}
}
// TEST CODE
public class CustomerItemValidatorTests {
@Mock // Mockito가 NamedParameterJdbcTemplate의 Mock과 테스트에 사용할 각 프록시를 생성한다.
private NamedParameterJdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
private CustomerItemValidator validator;
@BeforeEach
public void setUp() {
MockitoAnnotations.initMocks(this); // Mock 초기화
this.validator = bew CustomerItemValidator(this.template); // 인스턴스 생성
}
// ...
}아래 테스트 코드는 행동 주도 설계 스타일로 작성된 코드다.
// ex1.
@Test
public void testInvalidCustomer() {
// given
CustomerUpdate customer = new CustomerUpdate(5L);
// when
ArgumentCaptor<Map<String, Long>> parameterMap = ArgumentCaptor.forClass(Map.class);
when(this.template.queryFor0bject(eq(CustomerItemValidator.FIND_CUSTOMER), parameterMap.capture(), eq(Long.class))).thenReturn(2L);
this.validator.validate(customer);
// then
assertEquals(5L, (Long) parameterMap.getValue().get("id"));
}
// ex2.
@Test
public void testInvalidCustomer() {
// given
CustomerUpdate customerUpdate = new CustomerUpdate(5L);
// when
ArgumentCaptor<Map<String, Long>> parameterMap = ArgumentCaptor. forClass(Map.class);
when(this.template.queryFor0bject(eq(CustomerItemValidator.FIND_CUSTOMER), parameterMap.capture(), eq(Long.class))).thenReturn(OL);
Throwable exception = assertThrows(ValidationException.class, () -> this.validator.validate(customerUpdate) ) ;
// then
assertEquals("Customer id 5 was not able to be found", exception.getMessage());
}통합 테스트
통합 테스팅 환경 구성
testImplementation group: 'org.hsqldb', name: 'hsqldb', version: '2.7.0'
HyperSQL은 100% 자바로 구현된 DB로 인스턴스를 스풀링하기에 가볍기 때문에 통합 테스트에 적합하여 HyperSQLDB 인메모리를 사용한다.
@ExtendWuth(SpringExtension.class)
@JdbcTest
public class CustomerItemValidatorIntegrationTests {
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
private CustomerItemValidator customerItemValidator;
@BeforeEach
public void setUp() {
NamedParameterJdbcTemplate template = new NamedParameterJdbcTemplate(this.dataSource);
this.customerItemValidator = new CustomerItemValidator(template);
}
@Test
public void testNoCustomers() {
CustomerUpdate customerUpdate = new CustomerUpdate(-5L);
ValidationException exception = assertThrows(ValidationException.class, () -> this.CustomerItemValidator.validate(customerUpdate));
assertEquals("Customer id -5 was not able to be found", exception.getMessage());
}
@Test
public void testCustomers() {
CustomerUpdate customerUpdate = new CustomerUpdate(5L);
this.customerItemValidator.validate(customerUpdate);
}
}- @ExtendWuth(SpringExtension.class) = @RunWith(SptingRunner.class)
- @JdbcTest 어노테이션은 인메모리 EB를 생성하고 스프링 부트가 일반적으로 사용하는 데이터를 초기화 스크립트를 실행함으로써 초기 데이터를 적재한다.
- @Autowired를 통해 DataSource를 가져왔다면 setUp 메서드를 통해 validator를 생성한다.
스프링 배치 job과 step scope bean 테스트
스프링 배치는 step 내에서 Execution을 에뮬레이트하여 값을 주입하는 두 가지 방법이 있다.
두 가지 구현체 중에 StepScopeTestExecutionListener를 알아본다.
TestExecutionListener : 테스트 메서드 전 후에 수행되어야하는 일을 정의하는 스프링 api
StepScopeTestExecutionListener
- 테스트 케이스에서 팩토리 메서드를 사용해 stepExecution을 가져오고 반환된 컨텍스트를 현재 테스트 메서드의 컨텍스트로 사용
- 각 테스트 메서드가 실행되는 동안 stepContext를 제공
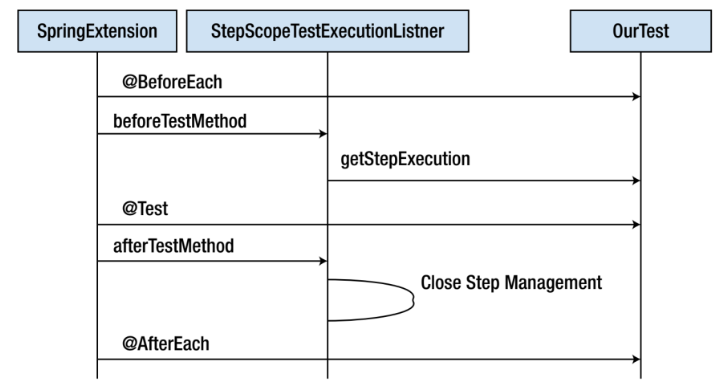
팩토리 메서드 getStepExecution은 새로운 stepExecution을 가져오기 위해 각 테스트 실행 전에 호출된다.
팩토리 메서드가 없다면 스프링 배치는 기본적으로 제공되는 stepExecution을 사용한다.
// ItemReader test
/*
reader가 읽을 테스트 파일
2,5,,,Montgomery,Alabama,36134
3,5,,,,316-510-9138,2
1,5,Rozelle,Heda,Farnill
*/
/*
STEP SCOPE
*/
@Bean
@StepScope
public FlatFileItemReader<CustomerUpdate> customerUpdateItemReader(@Value("#{jobParameters['customerUpdateFile']}") Resource inputFile) throws Exception {
return new FlatFileItemReaderBuilder<CustomerUpdate>()
.name("customerUpdateItemReader")
.resource(inputFile)
.lineTokenizer(customerUpdateLineTokenizer())
.fieldSetMapper(customerUpdateFieldSetMapper())
.build();
}
/*
TEST CODE
*/
@ExtendWuth(SpringExtension.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = {ImportJobConfigureation.class, // applicationContext를 만드는 클래스를 지정
CustomerItemValidator.class,
AccountItemProcessor.class})
@JdbcTest // DB제공
@EnableBatchProcessing // JobRepository와 연결(?)
@SpringBatchTest /* applicationContext에 자동으로 테스트할 수 있는 유틸리티 제공
* job이나 step을 실행하는 JobLauncherTestUtils 인스턴스
* JobRepository에서 JobExecutions를 생성하는 데 사용하는 JobRepositoryTestUtils
* step scop과 job scop bean을 테스트할 수 있는 StepScopeTestExecutionListner와 JobScopeTestExecutionListner
*/
public class FlatFileItemReaderTests {
@Autowired
private FlatFileItemReader<CustomerUpdate> customerUpdateItemReader;
// StepScopeTestExecutionListner를 사용해 step scop 의존성을 처리하려면 아래 메서드를 작성해야한다.
public StepExecution getStepExecution() {
// customerUpdateFile가 customerUpdateFile.csv 파일을 가르키도록 한다.
JobParameters jobParameters = new JobParametersBuilder()
.addString("customerUpdateFile", "classpath:customerUpdateFile.csv")
.toJobParameters();
// MetaDataInstanceFactory는 StepExecution이나 JobExecution 인스턴스를 생성하는 유틸리티 클래스
return MetaDataInstanceFactory.createStepExecution(jobParameters);
}
@Test
public void testTypeConversion() throws Exception {
this.customerUpdateItemReader.open(new ExecutionContext());
assertTrue(this.customerUpdateItemReader.read() instanceof CustomerAddressUpdate);
assertTrue(this.customerUpdateItemReader.read() instanceof CustomerContactUpdate);
assertTrue(this.customerUpdateItemReader.read() instanceof CustomerNameUpdate);
}
// ...
}// step test
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@JdbcTest
@ContextConfiguration(classes = {ImportJobConfiguration.class,
CustomerItemValidator.class,
AccountItemProcessor.class,
BatchAutoConfiguration.class})
@SpringBatchTest
// JdbcTest 어노테이션의 트랜잭션 기능이 동작하지 않게 비활성화 한다.
@Transactional (propagation = Propagation.NOT_SUPPORTED)
public class ImportCustomerUpdatesTests {
@Autowired
private JobLauncherTestUtils jobLauncherTestUtils;
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
private JdbcOperations jdbcTemplate;
@BeforeEach
public void setUp() {
this. jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(this.dataSource) ;
}
@Test
public void test() {
JobParameters jobParameters = new JobParametersBuilder()
.addString("customerUpdateFile", "classpath: customerFile.csv").toJobParameters();
JobExecution jobExecution = this.jobLauncherTestUtils.launchStep("importCustomerUpdates", jobParameters);
assertEquals(BatchStatus.COMPLETED, jobExecution.getStatus());
List<Map<String, String>> results = this. jdbcTemplate.query("select * from customer where customer_id = 5", (rs, rowNum) -> {
Map<String, String> item = new HashMap<>();
item.put("customer_id", rs.getString("customer_id"));
item.put("first_name", rs.getString("first_name"));
item.put("middle_ name", rs.getString("middle_name"));
item.put("last_name", rs.getString("last_name"));
item.put("addressi", rs.getString("address1i"));
item.put("address2", rs.getString("address2"));
item.put("city", rs.getString("city"));
item.put("state", rs.getString("state"));
item.put("postal_code", rs.getString("postal_code"));
item.put("ssn", rs.getString("ssn"));
item.put("email_address", rs.getString("email_address"));
item.put("home_phone", rs.getString("home_phone"));
item.put("cell_phone", rs.getString("cell_phone"));
item.put("work_phone", rs.getString("work_phone"));
item.put("notification pref", rs.getString("notification pref"));
return item;
});
Map<String, String> result = results.get(0);
assertEquals("5", result.get("customer_id"));
assertEquals("Rozelle", result.get("first_name"));
assertEquals("Heda", result.get("middle name"));
assertEquals("Farnill", result.get("last_name"));
assertEquals("36 Ronald Regan Terrace", result.get("addressi"));
assertEquals("P.0. Box 33", result.get("address2"));
assertEquals("Montgomery", result.get("city"));
assertEquals("Alabama", result.get("state"));
assertEquals("36134", result.get("postal_code"));
assertEquals("832-86-3661", result.get("ssn"));
assertEquals("tlangelay4@mac.com", result.get("email_address"));
assertEquals("240-906-7652", result.get("home_phone"));
assertEquals("907-709-2649", result.get("cell_phone"));
assertEquals("316-510-9138", result.get("work_phone"));
assertEquals("2", result.get("notification pref"));
}
}
}// jobLauncherTestUtils를 테스트 클래스에 주입한 상태에서 잡을 정의해야한다.
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@SpringBatchTest
@ContextConfiguration(classes = {JobTests.BatchConfiguration.class, BatchAutoConfiguration.class})
public class JobTests {
@Autowired
private JobLauncherTestUtils jobLauncherTestUtils;
}// JOB CODE
@Configuration
@EnableBatchProcessing
public static class BatchConfiguration {
@Autowired
private JobBuilderFactory jobBuilderFactory;
@Autowired
private StepBuilderFactory stepBuilderFactory;
@Bean
public ListItemReader<String> itemReader() {
return new ListItemReader<>(Arrays.asList("foo", "bar", "baz"));
}
@Bean
public ItemWriter<String> itemWriter() {
return (list -> {
list. forEach(System.out::println);
});
}
@Bean
public Step step1() {
return this.stepBuilderFactory.get("step1")
.<String, String>chunk(10)
.reader(itemReader())
.writer(itemWriter())
.build();
}
@Bean
public Job job() {
return this. jobBuilderFactory.get("job")
.start(step1())
.build();
}
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
return new EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder().build();
}
}
// TEST CODE
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@SpringBatchTest
@ContextConfiguration(classes = {JobTests.BatchConfiguration.class, BatchAutoConfiguration.class})
public class JobTests {
@Test
public void test() throws Exception {
// jobLauncherTestUtils를 테스트 케이스 내부의 정적 클래스 내에 정의해도 OK
JobExecution jobExecution = this.jobLauncherTestUtils.launchJob();
assertEquals(BatchStatus.COMPLETED, jobExecution.getStatus());
StepExecution stepExecution = jobExecution.getStepExecutions().iterator().next();
assertEquals(BatchStatus.COMPLETED, stepExecution.getStatus());
assertEquals(3, stepExecution.getReadCount());
assertEquals(3, stepExecution.getWriteCount());
}
}'Framework > spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| part2. 동시성 이슈의 해결 방법 (2+1)가지 (0) | 2023.09.06 |
|---|---|
| part1. 동시성 이슈의 해결 방법 (2+1)가지 (1) | 2023.09.05 |
| 클라우드 네이티브 배치 (0) | 2022.09.21 |
| #18 : Lombok (1) | 2020.07.22 |
| #17 : H2 database 연동 준비 (2) | 2020.06.13 |




